39
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain how sexual identification and orientation are protected by law
- Discuss the ethical issues raised in the workplace by differences in sexual identification and orientation
As society expands its understanding and appreciation of sexual orientation and identity, companies and managers must adopt a more inclusive perspective that keeps pace with evolving norms. Successful managers are those who willing to create a more welcoming work environment for all employees, given the wide array of sexual orientations and identities evident today.
Legal Protections
Workplace discrimination in this area means treating someone differently solely because of his or her sexual identification or sexual orientation, which can include, but is not limited to, identification as gay or lesbian (homosexual), bisexual, transsexual, or straight (heterosexual). Discrimination may also be based on an individual’s association with someone of a different sexual orientation. Forms that such discrimination may take in the workplace include denial of opportunities, termination, and sexual assault, as well as the use of offensive terms, stereotyping, and other harassment.
Although the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in United States v. Windsor (2013) that Section 3 of the 1996 Defense of Marriage Act (which had restricted the federal interpretations of “marriage” and “spouse” to opposite-sex unions) was unconstitutional, and guaranteed same-sex couples the right to marry in Obergefell v. Hodges (2015),
marital status has little or no direct applicability to the circumstances of someone’s employment. In terms of legal protections at work, the LGBTQ community is at a disadvantage because Title VII of the CRA does not address sexual orientation and federal law does not prohibit discrimination based on this characteristic. As of January 2018, twenty states prohibit sexual orientation discrimination in private and public workplaces and five more states prohibit sexual orientation discrimination only in public workplaces, not private ((Figure)).
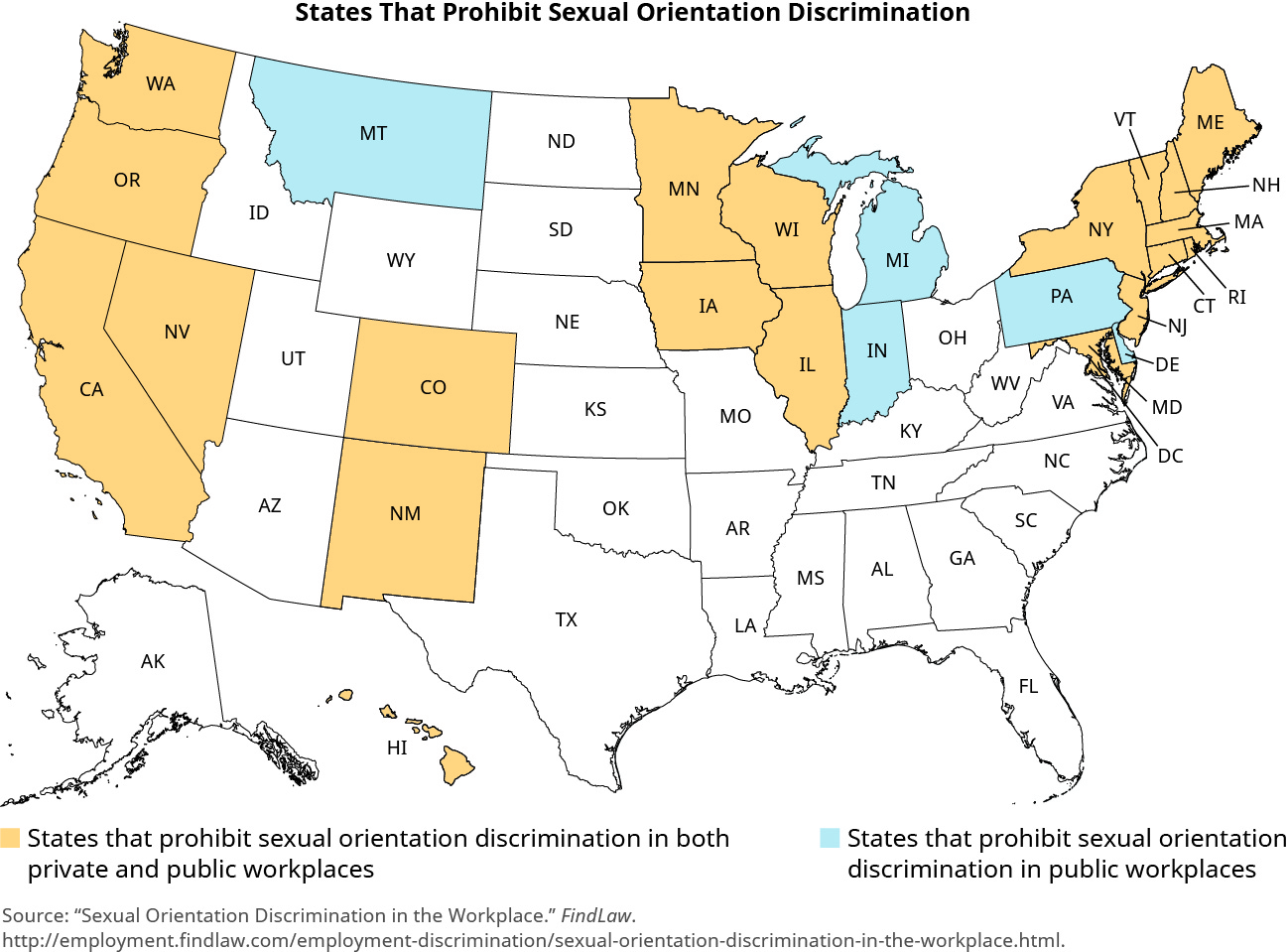
In those states that do not have applicable state laws, employees risk adverse employment action simply for their LGBTQ status or for being married to a same-sex partner. Although legislation to address these circumstances has been introduced in Congress in previous sessions, none of the bills has yet passed. For example, a proposed law named the Equality Act is a federal LGBTQ nondiscrimination bill that would provide protections for LGBTQ individuals in employment, housing, credit, and education. But unless and until it passes, it remains up to the business community to provide protections consistent with those provided under federal law for other employees or applicants.
Ethical Considerations
In the absence of a specific law, LGBTQ issues present a unique opportunity for ethical leadership. Many companies choose to do the ethically and socially responsible thing and treat all workers equally, for example, by extending the same benefits to same-sex partners that they extend to heterosexual spouses. Ethical leaders are also willing to listen and be considerate when dealing with employees who may still be coming to an understanding of their sexual identification.
Financial and performance-related considerations come into play as well. Denver Investments recently analyzed the stock performance of companies before and after their adoption of LGBTQ-inclusive workplace policies.
The number of companies outperforming their peers in various industries increased after companies adopted LGBTQ-inclusive workplace policies. Once again, being ethical does not mean losing money or performing poorly.
In fact, states that have passed legislation considered anti-LGBTQ by the wider U.S. community, such as the Religious Freedom Restoration Act in Indiana or North Carolina’s H.B. 2, the infamous “bathroom bill” that would require transgender individuals to use the restroom corresponding with their birth certificate, have experienced significant economic pushback. These states have seen statewide and targeted boycotts by consumers, major corporations, national organizations such as the National Collegiate Athletic Association, and even other cities and states.
In 2016, in response to H.B. 2, nearly seventy large U.S. companies, including American Airlines, Apple, DuPont, General Electric, IBM, Morgan Stanley, and Wal-Mart, signed an amicus (“friend of the court”) brief in opposition to the unpopular North Carolina bill.
Indiana’s Religious Freedom Restoration Act evoked a similar backlash in 2015 and public criticism from U.S. businesses.
To assess LGBTQ equality policies at a corporate level, the Human Rights Campaign foundation publishes an annual Corporate Equality Index (CEI) of approximately one thousand large U.S. companies and scores each on a scale of 0 to 100 on the basis of how LGBTW-friendly its benefits and employment policies are ((Figure)). More than six hundred companies recently earned a perfect score in the 2018 CEI, including such household names as AT&T, Boeing, Coca-Cola, Gap Inc., General Motors, Johnson & Johnson, Kellogg, United Parcel Service, and Xerox.
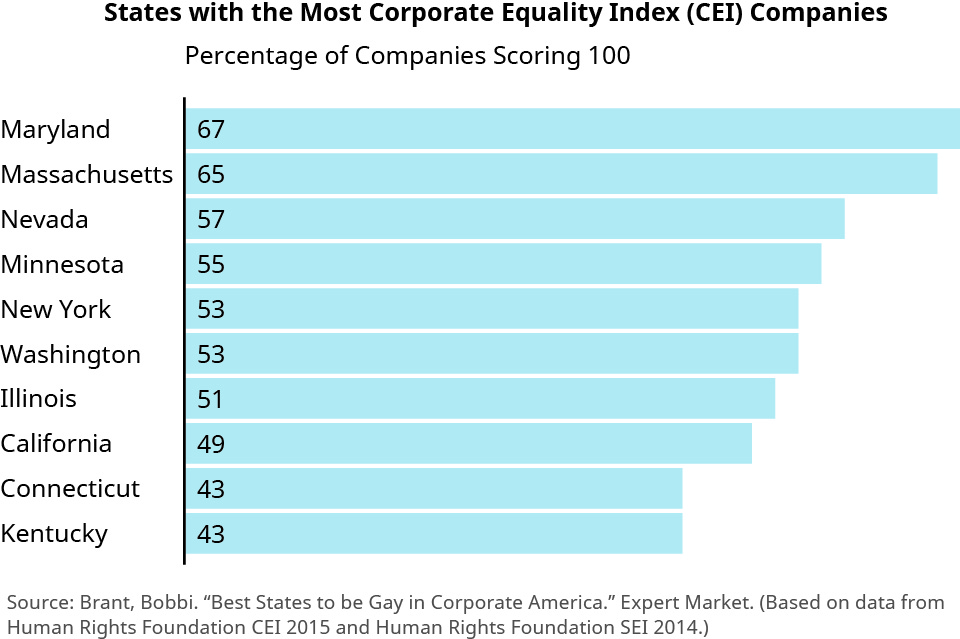
Read the Human Rights Campaign’s 2018 report for more on the Human Rights Campaign’s CEI and its criteria.
Another organization tracking LGBTQ equality and inclusion in the workplace is the National LGBT Chamber of Commerce, which issues third-party certification for businesses that are majority-owned by LGBT individuals. There are currently more than one thousand LGBT-certified business enterprises across the country, although California, New York, Texas, Florida, and Georgia account for approximately 50 percent of them. Although these are all top-ranked states for new business startups in general, they are also home to multiple Fortune 500 companies whose diversity programs encourage LGBT-certified businesses to become part of their supply chains. Examples of large LGBT-friendly companies with headquarters in these states are American Airlines, JPMorgan Chase, SunTrust Bank, and Pacific Gas & Electric.
Summary
Although about half the states prohibit sexual orientation discrimination in private and public workplaces and a few do so in public workplaces only, federal law does not. Successful companies will not only follow the applicable law but also develop ethical policies to send a clear message that they are interested in job skills and abilities, not sexual orientation or personal life choices.
Assessment Questions
Are individual states allowed to have laws protecting LGBTQ applicant or employee rights?
- Yes, but it is not really necessary because federal law already protects them.
- No, because it would violate federal law, which prohibits it.
- Yes, some states extend this protection because there is no law at the federal level.
- No, because the Supreme Court ruling in Obergefell v. Hodges now protects these rights.
C
True or false? Title VII of the Civil Rights Act prohibits discrimination based on sexual orientation.
False. Title VII of the Civil Rights Act does not address sexual orientation and federal law does not prohibit discrimination based on this characteristic.
Federal law does not currently protect LGBTQ applicants from discrimination in hiring. Are there any applicable state laws that do so?
Yes. Approximately half of U.S. states have local laws that provide protection even though federal law does not; however, some of those states prohibit sexual orientation discrimination only in public workplaces, not private ones.
Though federal law does not mandate it, do some companies nevertheless allow LGBTQ employees to extend insurance coverage to partners?
Yes. The law does not mandate or prohibit extending benefits to LGBTQ partners; it is up to the company.

